Matrox Design Assistant allows you to communicate with external
devices via the discrete I/O pins (auxiliary I/O pins) of your
runtime platform's input and output connectors , if the platform is
a Matrox smart camera, a Matrox 4Sight GP/GPm, or a PC equipped
with a Matrox Indio board. When using a PC runtime platform, Matrox
Design Assistant can also communicate with external devices via the
I/O pins of the input and output connectors of any connected
GigE/USB3 Vision camera that supports I/O. Matrox Design Assistant
can also use the additional I/O capabilities of runtime platforms
equipped with the Matrox Advanced I/O Engine.
You must specify which I/O pins your project will use and
configure how a signal should be transmitted/received on these
pins, using the
Platform Configuration dialog.
In addition, you can use
platform configuration binding or an
IOSettings step to change certain configuration settings of
the input and output signals during runtime.
The
IOReader step allows you to read the value of an auxiliary
input signal. The
IOWriter step allows you to set the value of an auxiliary
output signal.
Depending on the hardware available, auxiliary input signals can
be used with Matrox Design Assistant to perform the following
typical tasks:
-
Use an input signal to trigger a camera to grab an image.
-
Read the value of an input pin and have the flowchart perform an
operation according to that value (for example, check if a safety
door is closed).
-
Upon receiving an input signal, generate an output signal (often
a pulse) after a certain delay (for example, to trigger some
distance further down a conveyer from the part detector).
-
Take one or 2 rotary encoder inputs and use them as the clock
for position stamps and the delay of output signals.
-
Relay a trigger signal after having accurately latched the
time/position at which it arrived.
-
Use an input signal, along with 2 timers, as control for
outputting a pulse train.
Depending on the hardware available, auxiliary output signals
can be used with Matrox Design Assistant to communicate to an
external device or controller via:
Matrox Design Assistant only supports I/O with Matrox smart
cameras (for example, Matrox Iris GTR), Matrox PCs (for example,
Matrox 4Sight GPm, or PCs with a Matrox Indio board), and GigE/UBS3
Vision cameras that follow the GenICam Standard Feature Naming
Convention (SFNC v1.5).
When connected to a runtime platform, you can determine how many
I/O pins Matrox Design Assistant recognizes by clicking on the
List the Available
I/Os button in the IOs page of the
Platform Configuration dialog. This will state the number
of pins that are input, output, or bidirectional.
The following are the I/O capabilities available on different
platforms supported by Matrox Design Assistant.
|
Platform
|
Any PC
|
Any PC
|
Matrox 4SightGP
|
Matrox 4SightGPm
|
PC with Matrox Indio
|
Supported Matrox smart camera
|
|
Control (write value)
|
Flowchart Step
|
Unsupported GigE/USB3 Vision cameras
|
Supported GigE/USB3 Vision cameras
|
|
On/Off
|
IOWriter
|
–
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
Pulse duration in time
|
IOWriter
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
Pulse duration in rotary transitions
|
IOWriter
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
Delay in time relative to grab
|
IOWriter
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
Delay in position (for example, rotary encoder)
|
IOWriter
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
On/Off
|
CameraSettings (Edit GenICam)
|
Y
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
|
Features and Commands
|
CameraSettings (Edit GenICam)
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
X and Y
|
X and Y
|
X
|
|
Read value
|
IOReader
|
–
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
Read transition counts
|
IOReader
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
Input AB rotary encoder
|
PositionStamp
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X - Fully compliant camera. Use the
Platform Configuration dialog to configure this
component.
Y - Non compliant camera. Use the Feature Browser or a
CameraSettings step to configure this component (for
example, output ActiveExposure or Strobe).
PC Platforms - Note that third party I/O boards are not
supported. You can use a Matrox Indio board, I/O on the GigE Vision
camera, or network I/O expansion modules (for example, Modbus).
When you create a project that uses a certain number of I/O
pins, these settings are saved to the project. Consequently, a
project that uses I/O can only be deployed on a runtime platform
that supports I/O capabilities (see the Support for I/O
subsection of this section). However, this can be problematic when
a project is developed for a platform with a certain number of I/O
pins, and is opened while connected to a platform that has fewer
I/O resources.
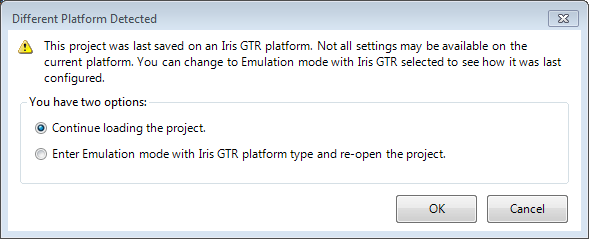
If you open a project that was originally developed using a
different platform than the one to which you are currently
connected, a warning dialog will appear, as shown below. You can
either emulate the platform on which the project was originally
developed, or continue opening the project. However, if you choose
the latter option on a platform that has fewer I/O pins than are
used in the project, you will see errors in the IOs page of the
Platform Configuration dialog and in the Errors
pane.
Alternatively, reconnect to a runtime platform with the correct
number of I/O pins, using the Platform menu.