Guides & Articles
Choosing the Best KVM Extender — Key Considerations
This guide provides an overview of KVM extension technology and explains the main points to be noted when evaluating KVM extenders. It also highlights the critical role that KVM extenders play in many environments, their benefits, the primary types of connections available with KVM extenders, and the characteristics of various transmission mediums.
What is a KVM extender?
A keyboard, video, and mouse (KVM) extender enables users to work on a computer from a distance. Typically, it is a set of transmitter and receiver appliances. The KVM transmitter unit is connected to the computer system and captures the peripheral signals such as universal serial bus (USB) for keyboard and mouse, audio, and video. These signals are extended to a remote user station where the monitors, keyboards, and mouse are powered by the KVM receiver unit. KVM extenders overcome the distance limitation of HDMI®, DisplayPort™, and USB cables and transport these signals anywhere from 15 feet to several miles away from the system.
Why do I need a KVM extender?
A KVM extender is useful wherever there is a need to control a computer from a distance—which could be for a variety of purposes. The most common reasons to use a KVM extender include user comfort and safety, centralization of equipment for security and easy maintenance, and enabling/improving collaborative efforts.
Ergonomic workplaces
A growing number of workplaces are adopting the use of KVM extenders to create more ergonomic work environments, by removing workstations that generate heat and noise and placing them in a server room, to free up space and improve working conditions. When a user needs to work on more than one system, using KVM extension with switching solutions declutters and optimizes desk space—since multiple computers can be controlled with a single set of displays, keyboard, and mouse.
Centralization of assets and security
Another important reason is to centralize the equipment in one location to simplify maintenance and improve security. Server rooms provide a temperature-controlled and dust-free location for computers, and protect them from corrosive elements that are in the environment such as moisture or salt. Locking equipment in server rooms is also a security measure. It limits access to these assets, and prevents hardware tampering and theft of critical information, among several other benefits.
Multi-user and multi-site collaboration
KVM extension and switching solutions are ideal when different users need to access the same computer to work from different locations (in the same building or across campuses). This also enables users to share their desktop on a video wall to visualize information for collaboration, and improve teamwork and decision making.
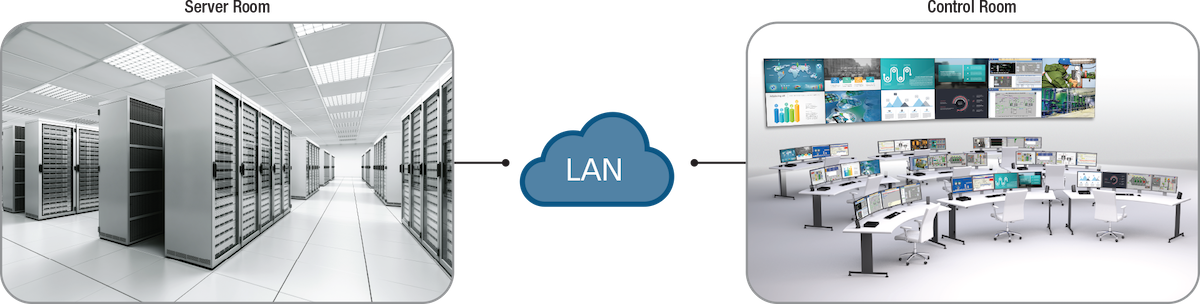
Where are KVM extenders used?
KVM solutions are deployed in a wide range of industries and control room applications to improve security, ergonomics, and collaboration—from industrial control rooms to military and defense command centers, airport management, transportation, emergency dispatch centers, post-production, broadcast, education and healthcare, to name but a few.
How does a KVM extender work?
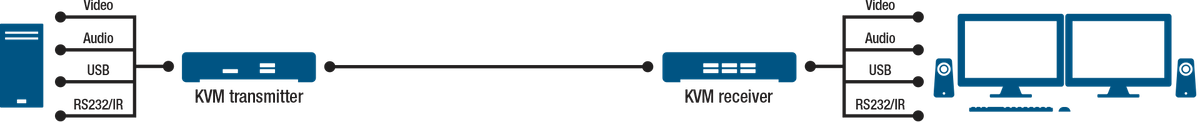
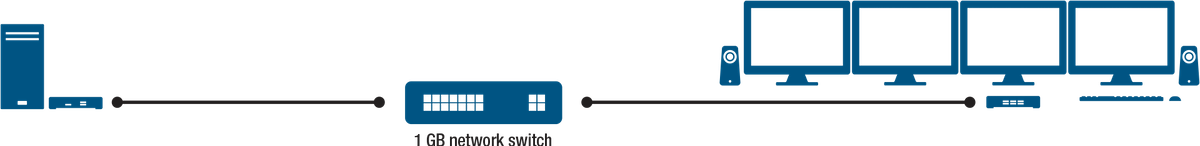
KVM extenders consist of a transmitter and receiver pair. A transmitter unit is located next to the computer system, and a receiver unit resides at the remote user station. The units communicate with each other over copper (such as CAT5e) or fiber optic cabling.
The KVM transmitter unit captures the input/output (I/O) signals from the computer—while the most common signals are video, audio, and USB for control, some models also extend RS232 and infrared (IR) signals. The KVM extender encodes these signals and uses either proprietary or internet protocol to transport them to the KVM receiver unit, which decodes these signals and powers the remote peripheral devices (such as displays, keyboard, mouse, and speakers). With IP KVM extenders, the information is transported as network packets over standard networking infrastructure.
Considering implementing a KVM solution?
See how Matrox KVM technologies can help
LEARN MORE ABOUT THE EXTIO 3 SERIES
KVM signal management
KVM extenders can operate as point-to-point devices, where a single transmitter unit communicates with a single receiver unit. They also enable the design of KVM matrix systems, where multiple systems can be accessed and controlled from multiple locations.
Point-to-point
In point-to-point KVM configurations, the transmitter unit is directly linked to the receiver unit via a wired connection, where the remote receiver unit can communicate with a single transmitter unit.

Many-to-many
More complex signal management and routing solutions are designed when KVM extenders are combined with KVM matrix switches, enabling users to access multiple source systems from multiple remote endpoints.
These solutions are often based on proprietary protocols to transmit information from point A to point B. This implies that a KVM extender from one vendor will not be interoperable with a KVM matrix switch from another vendor. Modern IP KVM products enable similar configurations by replacing the proprietary matrix switch with a standard networking switch.
KVM over IP
IP KVM products use internet protocol to transport information from point A to point B, converting the signal into packets and distributing them through standard network switches. This provides better scalability over traditional KVM extension technology.
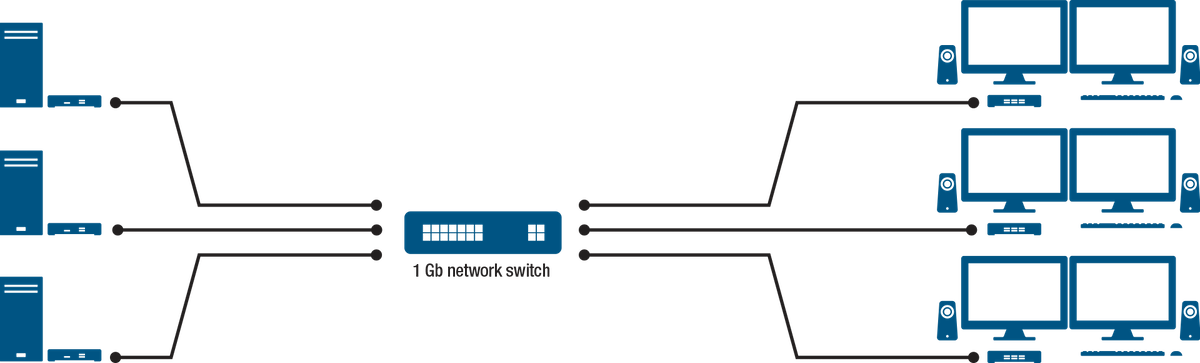
Commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) network switches effectively replace proprietary and higher cost KVM matrix switches, and using a KVM signal management software, easily route any source computer signal to any remote station. This drives down cost and improves standardization as it allows for the maximum leveraging of a common transport medium that is already being used in the environment. Another advantage is scalability. Networks by nature are scalable. With IP KVM solutions, one is no longer limited by the fixed numbers of ports that are available on the matrix switch—users can readily scale up by adding more systems and remote user stations, and easily expand the KVM network.
Key elements of choosing a KVM extender
Here are the most important things to take into
consideration when buying a KVM extender:
Identify video, USB, and audio requirements
As a general rule, the KVM product specifications should closely follow the requirements of the peripheral devices you need to access from a distance, such as the displays, keyboard and mouse, and other USB or audio devices.
Assess video connectivity and resolution
Early analog KVM extender models supported analog video signals (VGA). However, these analog models have limited resolution and distance support. Digital KVM extension solutions feature digital visual interface (DVI), high-definition multimedia interface (HDMI), and DisplayPort connectivity to overcome the limitations of earlier analog models.
DisplayPort and HDMI are the most common video connection standards available on professional workstation graphics cards and displays. The HDMI and DisplayPort specifications establish the maximum supported resolution per revision, the required bandwidth, and the corresponding high-bandwidth digital content protection (HDCP) revision. HDCP is a hardware encryption specification that protects digital content from being transmitted to non-compliant devices and prevents the unauthorized duplication of the content.
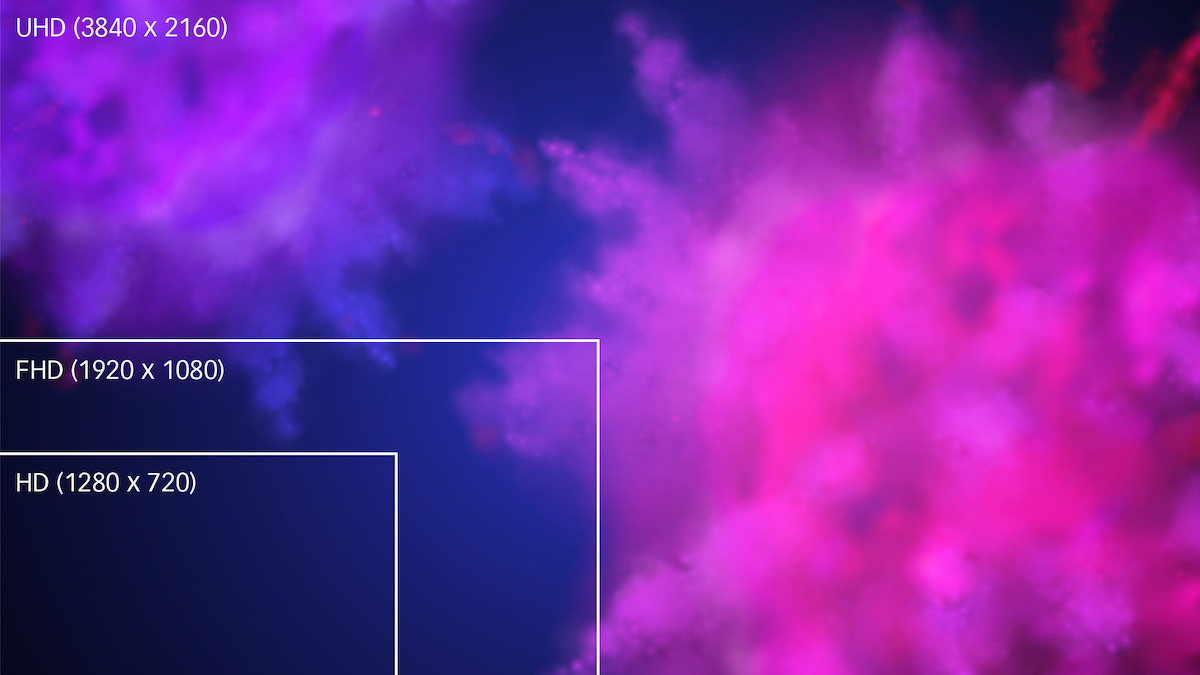
Resolution is the number of horizontal and vertical pixels (width x height) that can be displayed on a monitor. The higher the resolution, the clearer and sharper the image displayed. For example, 4K UHD resolution is a commercial standard that supports a resolution of 3840 x 2160 (creating an image approximately 4,000 pixels wide), compared to Full HD (FHD), which supports 1920 x 1080 pixels, and HD which supports 1280 x 720 pixels. Check that the KVM extender is capable of supporting the resolutions that your displays and source system support.

The following table lists the details of the latest DisplayPort and HDMI standards.
Table 1: Latest DisplayPort and HDMI standards
| Specification Standard | Year Released | Maximum Resolution | Maximum Resolution | Maximum Bandwidth | HDCP revision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DisplayPort 1.1a | 2008 | 2.5kp60 4Kp30 |
2560x1600 @60Hz 3840x2160 @30Hz |
10.8 Gbps | 1.1-1.3 |
| DisplayPort 1.2 DisplayPort 1.2 a |
2010 2012 |
4Kp60 | 3840x2160 @60Hz | 21.6 Gbps | 1.1-1.3 |
| DisplayPort 1.3 | 2014 | 5kp60 8Kp60 |
5120x2280 @60Hz 7680x4320 @30Hz |
32.4 Gbps | 2.2 |
| DisplayPort 1.4 | 2016 | 8Kp30Hz 8Kp60Hz1 4Kp120Hz |
7680x4320 @30Hz 7680x4320 @60Hz1 3840x2160 @120Hz |
32.4 Gbps | 2.2 |
| HDMI 1.3 HDMI 1.4ab |
2006 2010/2011 |
4Kp30Hz | 3840x2160 @30Hz | 10.2 Gbps | 1.1-1.4 |
| HDMI 2.0 HDMI 2.0a |
2013 2015 |
4Kp60Hz | 3840x2160 @60Hz | 18 Gbps | 2.2 |
| HDMI 2.1 | 2017 | 8Kp60Hz 4Kp120Hz |
7680x4320 @60Hz 3840x2160 @120Hz |
48 Gbps | 2.2 |
From the table, we can see that extending a 4K UHD display running at 60Hz requires a KVM extender that supports a video connector compliant with DisplayPort 1.2 (or higher), or with HDMI 2.0 (or higher). However, for a resolution of 2560x1600 or lower, a KVM extender compatible with DisplayPort 1.1 or HDMI 1.2 will work. An adapter can be used to convert an HDMI signal to DisplayPort or DVI, or vice versa.
The number of video signals that have to be extended per system also needs to be considered. High-performance KVM extenders are designed to support multi-display configurations without compromising user experience. Some models can extend up to four video signals over a single fiber optic of CATx cable, reducing infrastructure cost.
Ensure support for USB devices and other peripherals
KVM extenders can extend various kinds of USB devices. While keyboard and mouse are the primary USB devices, USB thumb, hard, or flash drives, as well as USB audio devices can be extended.
USB devices fall into three categories:
- USB HID devices — The USB human interface device (HID) class is a part of the USB specification for peripherals. It specifies a device class for HIDs such as keyboards, mice, joysticks, touch screens, and pen tablets. These devices typically operate at low speeds—at a 1.5 Mbps transmission rate.
- USB 2.0 devices — This class includes thumb drives, common access cards (CACs), audio devices, and video cameras. USB 2.0 can transfer data at a maximum rate of 480 Mbps.
- USB 3.0 devices — This class comprises hard drives and flash drives. USB 3.0 offers data transfer at a maximum rate of 800 Mbps.
USB 2.0 and 3.0 devices can further be categorized according to the type of transfer they support:
- Bulk transfers — These do not lose data and can reach higher speeds because they are able to utilize the bandwidth not used by other transfers, but there is no guaranteed minimum bandwidth. Among the devices that fall into this category are hard drives, thumb drives, and touchscreens.
- Isochronous transfers — These use a guaranteed fixed bandwidth for the reliable, real-time data transfer of audio and video I/O devices. Audio players and video cameras typically fall into this category.
KVM extenders may support some or all types of USB devices. Make sure that the KVM extender is capable of handling all the required types of USB and other peripheral signals for the installation.
Verify support for audio devices
Most KVM extenders have a combination of connectors to support both analog and digital audio devices. Line-in connectors can be used to connect an amplified analog audio source like an audio mixer, whereas 3.5 mm jacks are used for un-amplified audio signals such as a microphone or headphone. The USB ports with isochronous data transfer support can also connect digital audio devices or USB headsets. Both DisplayPort and HDMI video connectors can carry digital embedded audio from the system to the display.
Determine the infrastructure needs
Once all the signal connectivity requirements are identified, the next step is to look at infrastructure requirements. What distances need to be covered? What type of cabling is apt for the distances that need to be supported? Can existing infrastructure be used, or is there a need to run new cables? These are some of the major infrastructure-related decisions that need to be made.
Ascertain transmission medium: Distance and bandwidth
KVM extenders transport signals over CATx or fiber optic cables. The cable type used determines the bandwidth of the link as well as the distance covered.
- CATx—These cables are made up of multiple strands of copper wire that are twisted together, with four twisted wire pairs per cable: two to send data, and two to receive data. Data is transmitted via electrical signals sent through the copper cabling. CATx cables are often used in Gigabit Ethernet (GigE or GbE) local area networks (LANs). Typically, CAT5e cables support a maximum distance of 100 meters (328 feet) in point-to-point. KVM over IP installations benefit from longer distances over CATx cable by going through multiple routers and switches.
The following table lists the maximum distance supported in point-to-point configurations2. Longer distances are supported over IP operations.
Table 2: CATx cable types
| CAT5e | CAT6 | CAT6a | CAT7 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bandwidth | 1 Gbps | 1 Gbps | 10 Gbps | 10 Gbps |
| Maximum Frequency | 100 MHz | 250 Mhz | 500 MHz | 600 MHz |
| Maximum Distance | 100 m (328 ft) |
100 m (328 ft) |
100 m (328 ft) |
100 m (328 ft) |
- Fiber optic—These cables are made up of thin strands of optically pure glass that carry digital information with light instead of the electrical signals used with Ethernet, which makes them immune to electro-magnetic interference (EMI). Fiber optic cables also provide a quantum jump in distance supported compared to CATx in point-to-point—for example, fiber optic SFP+ cabling can cover up to 10 kilometers (6.21 miles).
There are two basic types of fiber optic cable, namely single-mode and multi-mode. Single-mode fiber optic cables use laser light to send signals and are thinner than multi-mode fiber optic cables. Multi-mode fiber optic cables use light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to send signals. Multi-mode cables are usually suitable for shorter distances—up to 550 meters (1804 feet).
Table 3: Fiber optic cable types
| Type | Core/Cladding Diameter | 1 Gbps Data Rate | 10 Gbps Data Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OM1 | Multi-Mode | (62.5/125 μm) | 275 m | 33 m |
| OM2 | Multi-Mode | (50/125 μmm) | 550 m | 82 m |
| OM3 | Multi-Mode | (50/125 μm) | 550 m | 300 m |
| OM3 | Multi-Mode | (50/125 μm) | 550 m | 400 m |
| OS1 | Single-Mode | (9/125 μm) | 5 km | 2 km |
| OS2 | Single-Mode | (9/125 μm) | 5 km | 10 km |
Transmission mediums have bandwidth limitations and higher resolution video signals invariably demand higher bandwidth. While CAT5e cables provide the necessary bandwidth support for extending uncompressed 1080p60 video, resolutions higher than 1080p60 will not be possible as they require more bandwidth than what these cables can support. For example, uncompressed 4K UHD resolution video (2160p60) requires upwards of 12 Gbps of bandwidth, whereas the maximum bandwidth supported by CATx cables is only 10 Gbps. A solution to this is KVM extenders that use some level of compression to reduce the data size, to enable it to fit the available bandwidth. Alternatives to using a compression technology include running multiple cables, or going with KVM extenders with higher transmission bandwidth, both of which could drive up infrastructure cost.
Pay heed to other important elements
The following are other considerations for KVM extenders that may have to be taken into account, depending on the application's requirements.
Performance
High image quality is of prime importance for many applications. For desktop applications, selecting a KVM solution that does not perform chroma sub-sampling to reduce the size of the video bandwidth and stays in 4:4:4—the best image quality possible—will deliver sharp text and fine lines. It is expected that KVM extenders also provide seamless access to remote systems; the keyboard and mouse responsiveness have to be exceptional—it needs to feel as if the user is working right next to the system.
The images given below display the difference in quality between true color 4:4:4 vs 4:2:0 with chroma sub sampling. The 4:2:0 image example clearly indicates how 4:2:0 chroma sub-sampling makes text look fuzzy to view and is not deliver an acceptable quality level for desktop applications.


Security
Security is one more major area to take into consideration while evaluating an IP KVM extension switching solution, where both the network design and the KVM extension product play vital roles. For example, make sure that the KVM product supports encryption and protects the information that is being transmitted over the network.
Improve environments for both computers and operators
KVM extension technology has been helping to create better office and industrial work habitats. When it comes to choosing a KVM extender, assess your infrastructure and workplace needs, and select a secure, flexible solution. Matrox offers KVM solutions that can integrate seamlessly into your existing infrastructure.
Footnotes:
